For a business to develop progressively and be effective, it is necessary to find weaknesses on time and identify shortcomings in the sales scheme; this will help you study the consumer journey by sales stages and draw up a special model based on it.
A sales funnel for e-commerce is a marketing model that illustrates the theoretical journey of a customer from getting to know a product to completing a deal; this is a tactical scheme, conditional and extremely simplified, which is a formalization of the step-by-step path of the ideal consumer (Consumer Journey).
In reality, buyers go to the sale in a non-linear way – they can return to previous stages, lose an opportunity or desire. However, a sales funnel is a must-have for any marketing concept, as it allows you to find problematic stages of sales and eliminate them.
The first model to describe the customer journey was developed in 1898 by E. Saint-Elmo Lewis. It is built according to the AIDA scheme; this is an abbreviation for the names of the stages that the client goes through:
- Attention. The consumer learns about the product through some source of information.
- Interest. The person becomes interested in the product; they are looking for additional information.
- Desire. A potential client has a desire to purchase a product.
- Action. A deal is made.
If a customer funnel describes the e-commerce customer journey, then a sales funnel describes the actions of a businessman:
- To convey information to a potential consumer.
- Make contact with the person who makes the decision.
- Hold a meeting and agree.
- Deliver the product and get paid.
E-commerce Funnels Types

The following funnels are distinguished by type:
- “From attraction to closing a deal” – shows the stages of primary interest, preliminary work, and the actual sale.
- “Sales only” – displays only the cycle of the transaction. May have quantitative or qualitative indicators. For example, count the number of visitors who have moved to the next stage or assess the quality of staff work at a particular stage.
- “Sale + service” – includes the stages that follow after the sale (delivery, warranty, assembly, etc.).
- “Cross-selling and additional sales” – after passing the sales stage, the funnel continues with overlapping and additional sales (consumables, service).
The sales funnel cannot be universal for all forms of business. It varies depending on the specifics of the product, the sales scheme, distribution channels, and the size of the business.
Here is what a B2B funnel might look like:
- cold calls – informing potential customers;
- presentation – the choice of a specific product;
- commercial offer – a desire to purchase a product or service;
- contract and invoicing – conclusion of the transaction;
- payment and shipment – closing the deal;
- repeat purchase – additional sales.
If a business works for ordinary people and has no competitors, then the chain is short: information – visit – payment. But marketing funnel for e-commerce would look like this:
- Internet advertising.
- Go to the site.
- Product selection.
- Adding to cart.
- Checkout.
- Payment.
- Receiving.
Best E-commerce Sales Funnel Guidelines

While funnels differ from one business segment to another, they are all built according to specific rules:
- If you are using multiple acquisition channels, create a funnel for each one; this is important since the consumer’s path in such cases will always be different, while the main “body” will contain the same stages.
- Funnel stages can coincide with business processes, or they can combine several. For example, billing by accountant and manager can be combined.
- Be clear about the boundaries of each step; this will clarify the e-commerce consumer journey.
- The same action can be placed at different stages of the funnel only if the goal has changed, for example, a cold commercial offer and an individual offer for a specific product.
- Note that the consumer can move along the funnel non-linearly: both forward and backward.
- Use CRM systems to automate work with e-commerce funnels.
So, the general strategy for phasing through marketing funnel for e-commerce can be summarized in five main points:
- Attract users who are not yet familiar with your business.
- Engage visitors who already know about the product’s existence.
- Provide information for those interested in buying.
- Convert interested users into buyers.
- Re-engage the core of the audience, those who have already become a client.
Let’s take a closer look at each step in the funnel, and along with it, the marketing techniques that lead to increased sales.
Step 1: Engage Your Audience
The consumer cannot purchase your product without knowing about its existence and will not want to buy it if they do not have trust. Therefore, you need to create a name for your brand, to strengthen it as an industry leader. Where to start building your best e-commerce sales funnel?
Blog. Using a blog on a site selling goods or services, you can inform the consumer about your products, as well as touch on topics that are indirectly related to your business. For example, when offering sports equipment, tell the reader about the protein diet or the allowable stress on the body.
Social networks. Consumers turn to social media for reviews, recommendations, reviews. They expect the business to be available for questions on Facebook, open to feedback. Video tutorials on Youtube sometimes help to quickly solve the most difficult problems. A photo review on Instagram reveals the company’s life from the inside, allowing you to “bring” a potential client closer to the brand.
Advertising. At first, business is often limited to the first two points. But in a competitive environment, where it takes more time to reach the TOP of search engines, sites use PPC (Pay per Click) campaigns for the first step in the sales funnel; this is where you pay per click on your ad, banner on other sites, or Google.
Step 2: Engage Visitors
Once the user is familiar with your business, proceed to the second stage of building a sales funnel. Encourage them to perform simple actions on the site even before they make a purchase decision.
A good idea is to use a CTA. For each page, select the purpose for which it was created. What should a visitor do on this page? Download the app or watch the video? Fill out the contact form? Place some Call-to-Action buttons on the page that will lead to this goal.
Landing pages are pages that solve one problem. Traffic from other pages of the site is redirected here. Landing page creation is the top priority for launching a sales funnel. Such a landing page can be both an intermediate stage of the funnel and the final one.
Step 3: Product Selection, Decision-making Stage
So, you have drawn attention to your product, created communication channels with the consumer. Now what?
The next stage of the e-commerce purchase funnel is to educate the consumer and give them knowledge about your product or service. Users have questions, and your task is to answer them.
The ultimate goal of this stage is to assess the prospects for interaction. You help potential clients understand if your product is right for them. At the same time, you want to know if the user is right for you.
What Methods Will Help Here?
- E-mail newsletters. If you have collected a sufficient number of e-mail addresses on the site and created a database, you can start building a dialogue via e-mail. Submit training articles through this channel, answers to the most common questions. Also, e-mail newsletters are suitable for sending commercial offers, price lists, documents, presentations, etc.
- WhatsApp mailings. This communication method is used for a well-developed customer base, where telephone numbers are collected. As a rule, the user shares their contact number when ordering, after purchasing, and when they have a sufficient level of trust in the company. Therefore, WhatsApp mailings are more often used to stimulate repeat purchases with service notifications, last-minute offers, and urgent messages.
Step 4: Purchase
On average, customers should be offered a product 7 times before they are ready to buy! Therefore, give the potential customer a clear opportunity to make a purchase and do it more often.
How? Follow these tips:
- It is important for e-commerce to offer a product consistently at every stage of visiting the pages of the site. Do not expect the customer to find the product in the online store and deal with the order. Simplify the lives of your visitors. Make it as easy as possible for their journey to purchase, streamline the checkout process. Give easy access to an online chat to quickly resolve issues.
- Choose the best time for your mailings. A timely message about a sale or promotional offer often results in a quick purchase; this is especially true when changing seasons, before holidays, or on important dates.
- Highlight those users who have already gone through all the planned steps in the sales funnel but have not yet made a purchase. Develop your system of markers and signals for this through a CRM system, using tags on the site. For example, you can conduct triggered mailings for those who abandoned the cart without payment.
FAQ
- Remember that every customer must go through all the stages of the funnel.
- Find the bottleneck (the bottleneck where you lose the largest number of customers) and fix the situation.
- Expand the walls of the funnel: work to ensure that at each stage, there is an increase in the number of those consumers who pass further.
- Look for the most converting groups of people, sales channels, and products, and then direct the efforts of managers to those areas.
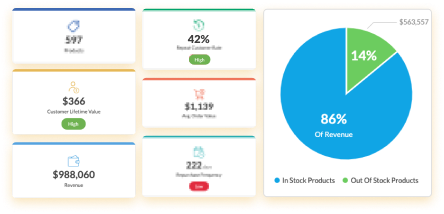
- conversion by stages and periods;
- key performance indicators for managers;
- the duration of the transaction and each stage;
- funnel throughput;
- average check of the transaction;
- the number of incoming and closed contacts.
In order not to configure everything yourself and to make it easier for marketers, you can use special services. AdScale will become your best friend for your business promotion.
The most common mistakes when creating an e-commerce purchase funnel:
- Design the “perfect” funnel. To get started, you must create a simple, working diagram. As soon as you get the first experience, you can start improving it.
- Highlight unnecessary steps. You should track only those actions that carry meaning.
- Linger on the stage. Don’t just focus on potential opportunities. Consumers must go through all the steps.














 ,
,